Categories of consumers of heat supply
The rules and regulations apply to the design of heat networks from collectors to locking outlets of heating points of residential (non-residential) buildings. Thermal networks mean structures of all types: houses, pumping stations, heat supply points, chambers, drainage devices, etc.
Design, reconstruction, re-equipment, modernization of buildings must provide for the norms established by law. The rules provide for the interaction of all parts of the STC (centralized heat supply system).
Categories of consumers of heat supply
- The first group are consumers who do not interrupt the supply of the calculated amount of energy, do not allow the outdoor temperature to drop below the state standard. These are medical, school institutions, places of cultural recreation (museums, galleries), production of specific areas (chemical plants, coal mines, etc.).
- The second group of consumers of thermal energy - suggest a decrease in the temperature of residential premises during the heating period. Time indicators - no more than 54 hours. Industrial buildings - up to 9 degrees, residential - 12 degrees Celsius.
- The third group is consumers who are not related to the first and second.
The classification of heat networks is divided into 3 subgroups: distribution, quarterly, main. Branches to separate structures are separated from the first and third (distribution, main) branches. The procedure for dividing networks takes place within the framework of an operational project by the relevant organization.
emergency situations
Heat supply sources or heat networks operating in emergency mode must provide consumers with:
- The first category of reliability (heat is supplied in full).
- Supply of thermal energy of the second, third category of consumers, for ventilation, heating (according to the agreement of the parties on the established mode of steam, hot water supply).
In case of unforeseen circumstances, the parties conclude an agreement on emergency operation of ventilation systems that are not switched off. If it is impossible to shut off the water supply (hot water), the document prescribes the average consumption of heat resources per day.
There are acts of technological, emergency armor, concluded with consumers brought into the mode of limiting the supply of thermal energy. Reservation emergency represents the minimum waste of heat carriers. The technological process is completed, the personnel and the environment are provided with a safe stay on the territory of the enterprise.
Hot water supply systems, ventilation, air conditioning of heated premises are not included in emergency armor. This happens in the case of their safe operation, without risk to human life. Technological reservation implies the smallest indicator of heat consumption (heat carriers), as well as the time frame that the subscriber needs to safely complete the production process.
The equipment is turned off after the completion of the cycle of work. The load indicators of the restrictive schedule are indicated in the heat supply contract for consumers. Activities related to the decision to ensure the established restrictions, notification of operating personnel, are carried out by the subscriber concluding the call.
Reservation
Possible options for maintaining reserves:
- Duplicated schemes of heat sources are used to maintain the established level of emergency readiness of power structures.
- Mandatory availability of backup equipment.
- Acquisition and implementation of storage tanks.
- Additional pumping, pipeline devices.
- Introduction of a scheme of mutual redundancy of heat centers, adjacent networks of centralized provision.
- Combining two or more heat sources for a joint result.
Decrease in the indicator of quality of heat supply service
According to the established system for adding new subscribers to the heat supply networks, the temperature graph reduces the indicators to 60 degrees. The period of seasonal transition along the lower cut provokes overheating (overheating) of the premises. It is impossible to increase the set temperature, due to the lack of heat regulators, special equipment (pumps, heat indicators regulators) at the points. 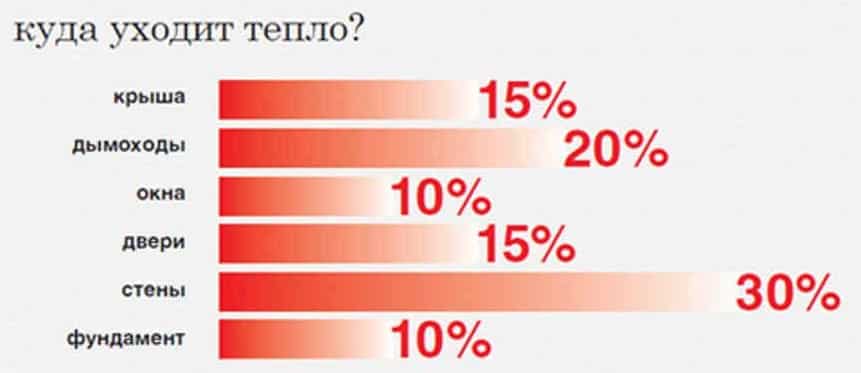
The source specified by the consumer does not provide a coolant, more than 95 degrees of heat. "Temperature shelf" (cut) provides a standard temperature for hot water supply. The decrease in strength and reliability of the heat supply scheme provokes a reduced level of energy quality.
Measures to ensure work in an emergency situation
There is the concept of "system survivability", which means the preservation of a normal workflow in extreme situations. Organization of actions in practice includes:
- Ensuring fluid circulation inside thermal installations.
- Pumping out water from a distribution type system (main, transit thermal passages).
- Heating, refilling the heat supply system during the period of repair work, restoring the functioning of heat networks after an emergency.
- Mandatory verification activities (equipment reliability, redundancy quality).
- Increasing the load against surfacing when channels are flooded.
The listed operations are coordinated with the local administrative body, municipal institution, administration. Employees of the enterprise are notified. The mode, the fail-safe schedule and the heat supply restrictions are drawn up before the activation of the heating season.